Disable a Phase
Learn how to disable specific phases in the MoveData Pipeline execution lifecycle to omit processing specific data for your organisation's requirements.
Overview
The guide demonstrates how to disable a phase in a pipeline from executing. This example will focus on disabling the recurring phase. This can be done when an organisation does not want a donation to be parented by a recurring donation record.
Implementation
To disable a phase, you will need to create an entry in the Pipeline Metadata object. This can be done by navigating within Salesforce to Setup -> Custom Code -> Custom Metadata Types and managing the records for the MoveData Pipeline Settings (movedata__MoveData_Pipeline__mdt).
For our example, we will disabling the recurring phase so we will need to get the correct key for the Recurring Disable Phase for the Donation pipeline. This can be found in the donation-pipeline under Pipeline Metadata. The correct key for this example is PIPELINE_DONATION_RECURRING_DISABLE.
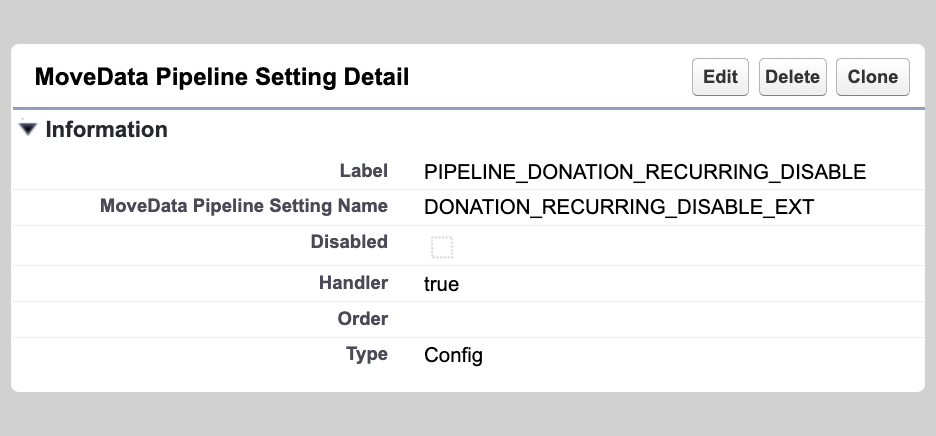
You will need to create a new entry with the following details:
| Field | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Label | PIPELINE_DONATION_RECURRING_DISABLE |
The key used by the pipeline to reference the configuration. |
| MoveData Pipeline Setting Name | A friendly name for you to determine. | |
| Disabled | [Unchecked] | MoveData not see the config entry when checked. |
| Handler | true |
Must be set to true to disable the stage. |
| Order | Ignored when disabling a stage. | |
| Type | Config |
Directs MoveData to read the Handler as a config value. |
Outcome
When a recurring phase is successfully disabled, you'll observe:
- Execution Logs: The MoveData execution log will show "Phase Skipped" entries for disabled phases, confirming the configuration is working correctly.
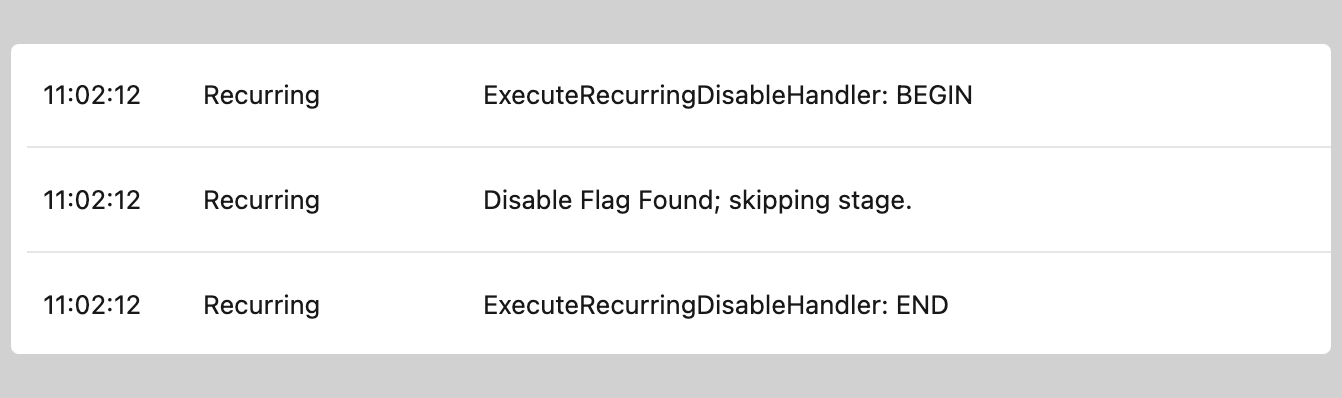
- Data Output: Records will be created according to the remaining enabled phases, with relationships and hierarchies adjusted accordingly.
| Before | After |
|---|---|
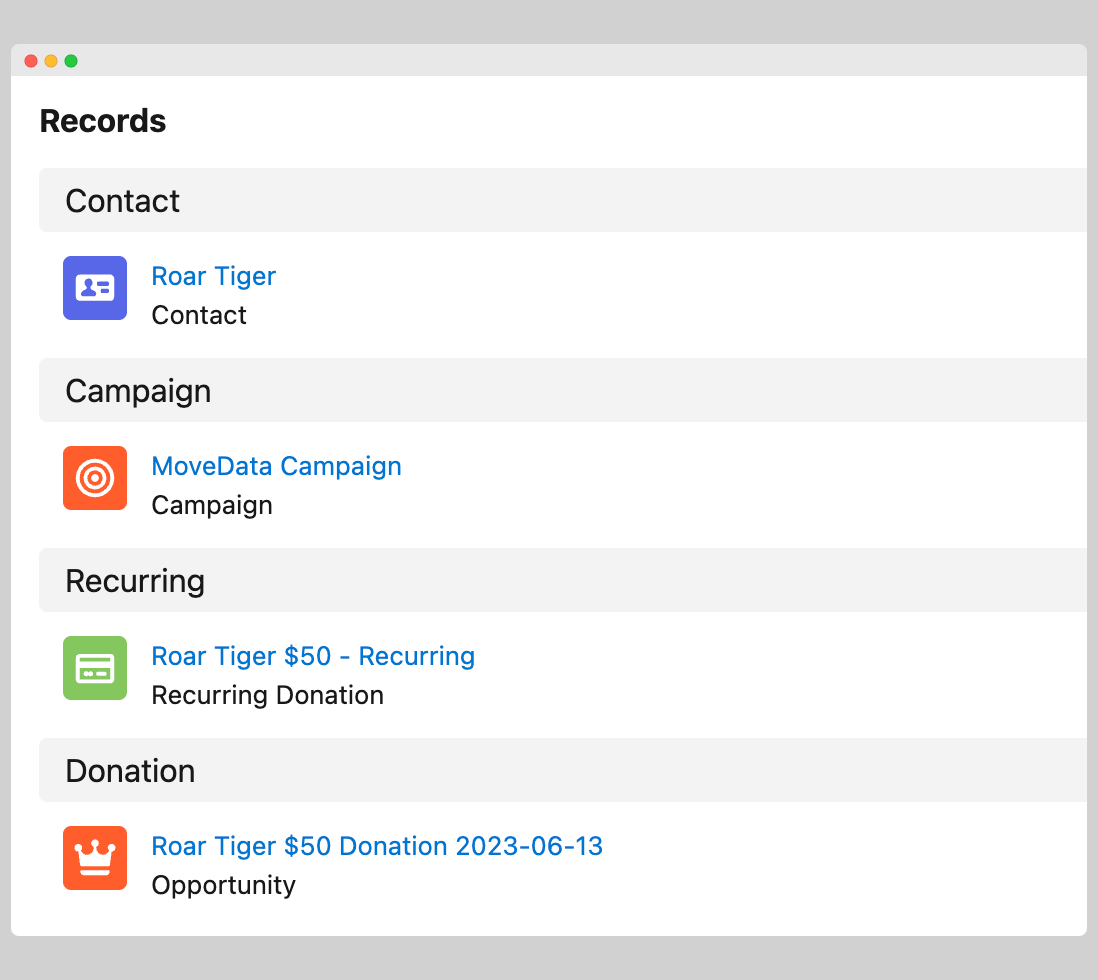 |
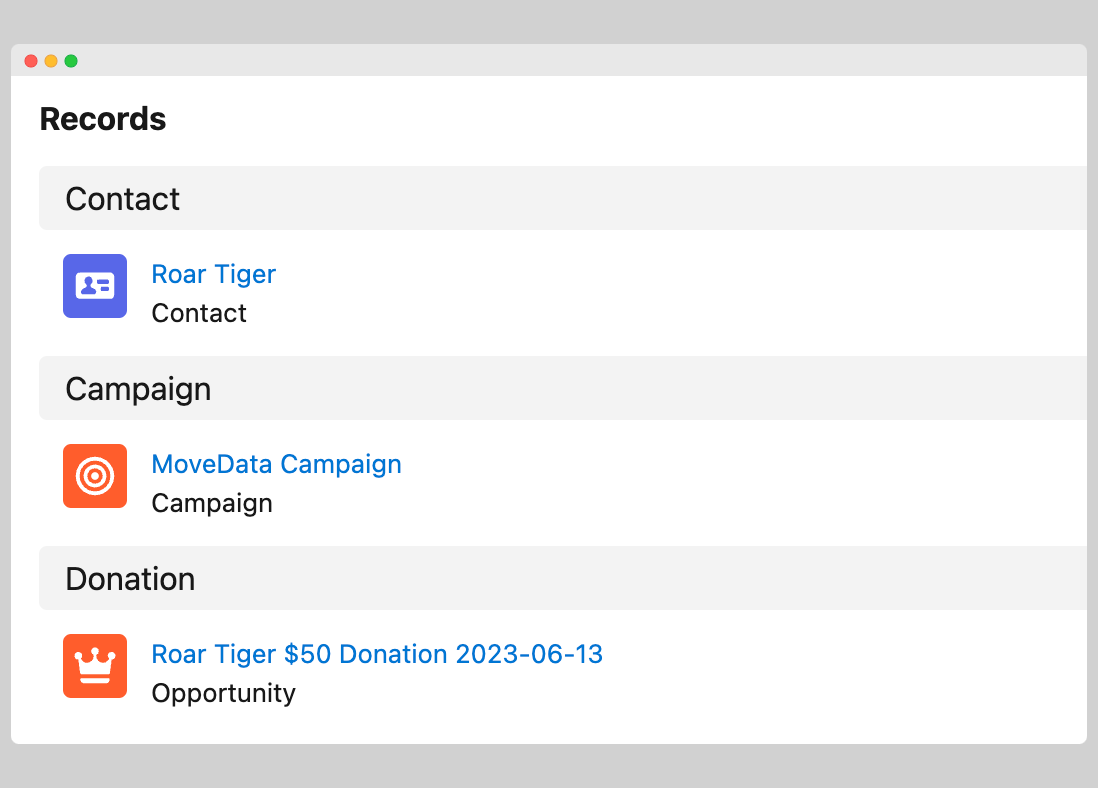 |
Validation and Troubleshooting
After implementing phase disabling:
- Monitor execution logs for "Phase Skipped" confirmations
- Review created records to ensure expected data structure
- Test with sample notifications before processing production data
- Verify multiple notification types still function with modified configuration